Dear traders, in our previous articles, we discussed the indispensable benefits of fundamental analysis in financial trading. Many events occurring worldwide and spreading news can directly impact the market. We can also add the information shared by International Credit Rating Agencies (ICRAs) to the news that causes price fluctuations in financial markets.
International Credit Rating Agencies (ICRAs) are independent
organizations that assess the credit risk of countries and companies and assign
credit ratings. The most well-known ones are Moody's, Standard & Poor's
(S&P), and Fitch Ratings. These agencies provide market participants with
information about the risk levels of debt instruments. Credit rating agencies
determine a credit rating by analyzing the financial status, debt levels,
repayment history, and future borrowing risks of borrowers. Credit rating
agencies conduct risk assessments based on analyses of financial conditions,
economic data, political stability, and other factors. These assessments are
expressed in the form of ratings consisting of letters and symbols. See the
example below:
 |
| Leading Credit Rating Agencies and their Rating Systems. |
Credit ratings give investors a general idea about the ability of borrowers to repay their debts. The highest credit rating is AAA, which means that the borrower has a very strong capacity to repay their debts. The lowest credit rating is D, which indicates that the borrower has a very low capacity to repay their debts.
Criteria for Determining Credit Ratings
Credit rating agencies evaluate various economic, financial,
and political criteria when determining the credit ratings of countries. The
downgrade or upgrade of a country's credit rating is based on the following
criteria:
Economic Factors:
Among the evaluation criteria, the economic performance of
countries is paramount. The size and growth rate of the economy are primarily
measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Additionally, macroeconomic
indicators such as inflation rate and unemployment rate are also assessed. The
diversification of the country's economy and the sectors it relies on are
analyzed as well.
Financial Factors:
The financial status is influenced by criteria such as the
country's debt level, budget balance, and debt repayment history. Additionally,
factors such as the borrower's debt burden, profitability, and cash flow are
analyzed. The government's income and expenditure balance, budget deficits or
surpluses, debt level, and debt management are used in determining credit
ratings. The central bank's foreign exchange reserves and exchange rate
stability, fiscal discipline, tax collection capacity, and spending policies
are also among these criteria.
Political and Institutional Factors:
Political risks such as the country's political system,
institutional structure, and rule of law are analyzed. Factors like the level
of corruption, legal system, and regulatory framework affect the quality of
governance. Among these criteria are geopolitical risks, including regional or
international conflicts and risks.
Other Factors:
Criteria such as the country's natural resource wealth and
their management, income distribution and social welfare indicators, and the
balance between imports and exports can also be evaluated.
Credit rating agencies evaluate the financial status, debt levels, repayment histories, and future debt repayment abilities of governments and companies seeking to borrow. Based on these evaluations, a "credit rating" is assigned to the entity seeking to borrow.
The Effects of Changes in Country Credit Ratings on Financial Markets
Downgrades of countries' credit ratings by international
credit rating agencies can have a series of critical impacts on financial
markets. These effects can influence financial markets and economic activities
both directly and indirectly. The borrowing costs for a country with a
downgraded credit rating increase. Investors, perceiving a higher risk of
default, demand higher interest rates for lending. This leads to a decrease in
the prices of government bonds and other debt instruments, and an increase in interest
rates. The currency of a country with a downgraded credit rating may depreciate
as investors perceive increased country risk. This can lead to higher prices
for imported goods and rising inflation. On December 1, 2023, Fitch rated the
United Kingdom's credit rating as AA- with a negative outlook. This resulted in
the depreciation of the British Pound. See the graphs below:
 |
| UK Credit Rating on December 1, 2023. |
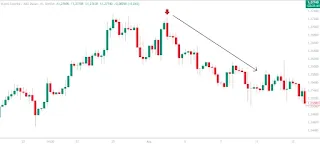 |
| UK Credit Rating and Sterling's Performance. |
A low credit rating can undermine investor confidence and
lead to a decrease in foreign investments into the country. This can cause
declines in stock markets and fluctuations in exchange rates. Shares of
companies operating within the country may lose value due to the increased
risks. In 2022, Standard & Poor's rated France's credit outlook as
negative, resulting in a decline in the France 40 Index. Please refer to the
chart provided for visual representation:
 |
| France Credit Rating on December 2, 2022. |
 |
| Impact of France's Credit Rating on France 40 Index |
Moody's positively evaluated Turkey's credit rating in
January 2024. As a result, many indices and stocks on the Borsa Istanbul,
including the BIST 100 Index, gained value. For example, refer to the chart
below for more details:
 |
| Turkey's Credit Rating Improved by Moody's in January 2024 |
 |
| BIST 100 Rallies After Credit Upgrade. |
The examples above demonstrate that credit rating downgrades
can have significant and negative short-term effects on currency and stock
markets, while credit rating upgrades can lead to positive outcomes. However,
in the long term, credit rating downgrades can encourage governments to
implement fiscal discipline and structural reforms, contributing to economic
strengthening and market recovery. These effects can vary depending on the
country's current economic conditions and the response to implemented policies.
The decisions made by credit rating agencies can prompt countries to reevaluate
their economic policies and take necessary measures to ensure macroeconomic
stability.
Never forget: Trading in financial markets is not a game. To succeed, you need a specific strategy and effective risk management. Fundamental analysis is an integral part of trading alongside technical analysis. Always prefer to trade using only a small portion of your capital (2-5%).